Comprehensive Dentistry in Seattle, WA
We work hard every day to help all of our patients feel comfortable and confident in our care. Our treatment plans are always customized based on the patient sitting in front of us, and we never push unnecessary services that we don’t truly believe in. Whether you’re in need of a routine cleaning or an advanced specialty treatment, our team is here to help. Contact us today!
Contact Us

Preventive Dentistry
Preventing dental issues before they occur is always ideal. Our practice offers a variety of excellent preventive services designed to help keep tooth decay, gum disease, and dental trauma at bay.
- Routine Cleanings & Exams
- Fluoride Treatments
- Dental Sealants
- Oral Cancer Screenings
- Halitosis Treatment
- Laser Gum Therapy
- Arestin® Gum Treatment
- Athletic Mouthguards
- Nightguards (For bruxism)
- TMJ/TMD Therapy
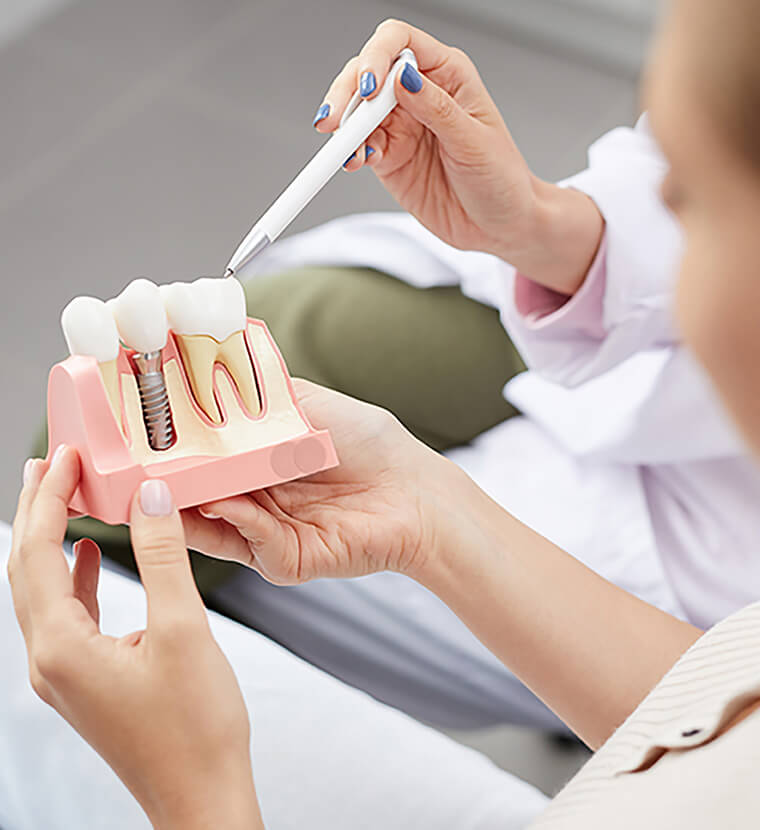
Restorative Dental Care
Sometimes, our smiles need a little extra TLC. Our restorative treatment plans are designed to treat dental issues quickly and effectively to have our patients smiling big again in no time.
- Composite Fillings
- Dental Crowns & Bridges
- Root Canal Therapy
- Full & Partial Dentures
- Implant-Supported Dentures
- Dental Implants
- Dental Extractions
- Wisdom Teeth Removal
- Bone Graft Procedures
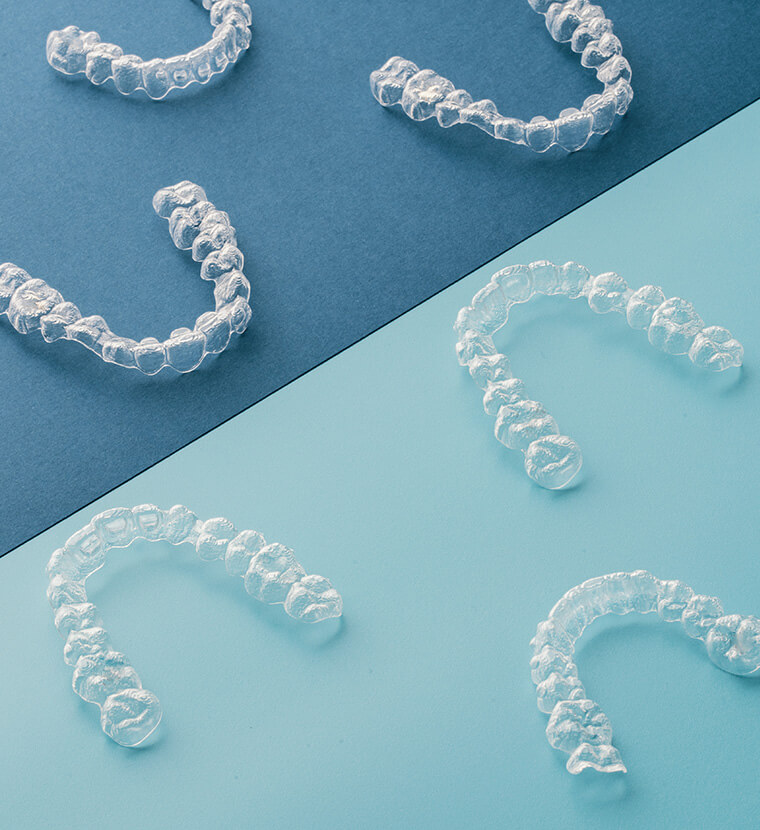

Cosmetic Services
Ever wish your teeth could be straighter, brighter, or more uniform? Our team would be glad to create a custom cosmetic treatment plan to help you achieve your smile goals.
- Professional Teeth Whitening
- Traditional Veneers
- Invisalign® Clear Aligner Therapy

Dental Sedation
Dental sedation is a safe and effective way to feel more comfortable and relaxed in the dental chair. If you’re interested in either of our sedation options, our team can discuss them with you and add the appropriate service to your treatment plan.
- Nitrous Oxide
- Oral Conscious Sedation
